This is Part 5 in my Configuring 802.1x Authentication for Windows Deployment series. Be sure to check out all of the other parts.
A few months ago, when I published the first 4 parts on this series, I was unaware that there was a web service available for managing Cisco ISE, which is the NAC that I have to work with in my environment. I was fortunate to meet with a peer who works nearby and he shared a script demonstrating how to interact with the Cisco ISE External RESTful Service (ERS) to dynamically whitelist devices when WinPE starts for Bare Metal OSD and inside an SCCM/ConfigMgr Task Sequence for In-Place upgrades. I built a script to use some of the newer features inside the ISE 2.2 service and includes logic to work with PowerShell 3.0 since most of my environment is still on Windows 7 and the Invoke-RestMethod and Invoke-WebRequest cmdlets don’t work properly in PowerShell 3.0. My plan is to replace all of the things the components that I built in the first 4 parts of this series with this script. Some of the steps I describe were completed by my ISE administrator. I don’t have access to the admin console, so I have limited information about how some items are configured. Please let me know if you get stuck and I can ask for better information.
Please note, the goal of this script is to give you the framework to build a solution for your needs and to provide one more set of tools to work with. It is not designed to be one-size-fits-all.
The Steps
- Enable ERS in ISE, Create an auto-purging whitelisting group in ISE and configure ISE to accept traffic from WinPE
- Test the whitelisting PowerShell script standalone
- Update your Boot WIM to include the whitelisting PowerShell script
- Update your In-Place Upgrade Task Sequence to run the whitelisting PowerShell script before the OS upgrade.
Enabling ERS on your ISE Server
Before you begin configuring ERS, here are a few things that I learned.
You must use an ISE built-in account, not a domain authenticated account.
You must use an ERS admin account. The ERS user account doesn’t have access to the ERS.
A great tool for testing the API is Postman or you can use the browser extensions referenced in the article below.
Start Here - This guide will walk you through configuring ERS on your server. Here is a PDF version of it in case the source ever changes. Next, have your ISE administrator create a new endpoint Group. You should configure the group to automatically remove endpoints after 24 hours. This will prevent failed devices from being orphaned in the group. Additionally, the restricted DACL needs to be configured to redirect traffic to the ISE server’s primary admin node (Per our admin. Not sure how he did this…).
Whitelisting MAC Addresses
I originally intended to build a full PowerShell module to able you to fully manage ERS with PowerShell but it just turned into a huge undertaking so I decided to just go with the most important bits. The script has examples in the comments at the top, so it should be straightforward to execute. Note 1: The ISEServerList.txt file is used to map Gateways to ISE Servers for locations that have several ISE servers (we do). If you only have 1 server, use the -Server parameter on your command line.
Note 2: The script will grab the currently active MAC address and whitelist it. You can use the -MACAddress parameter to specify a specific MAC Address if required.
The script performs 3 main functions based on the parameters that you provide.
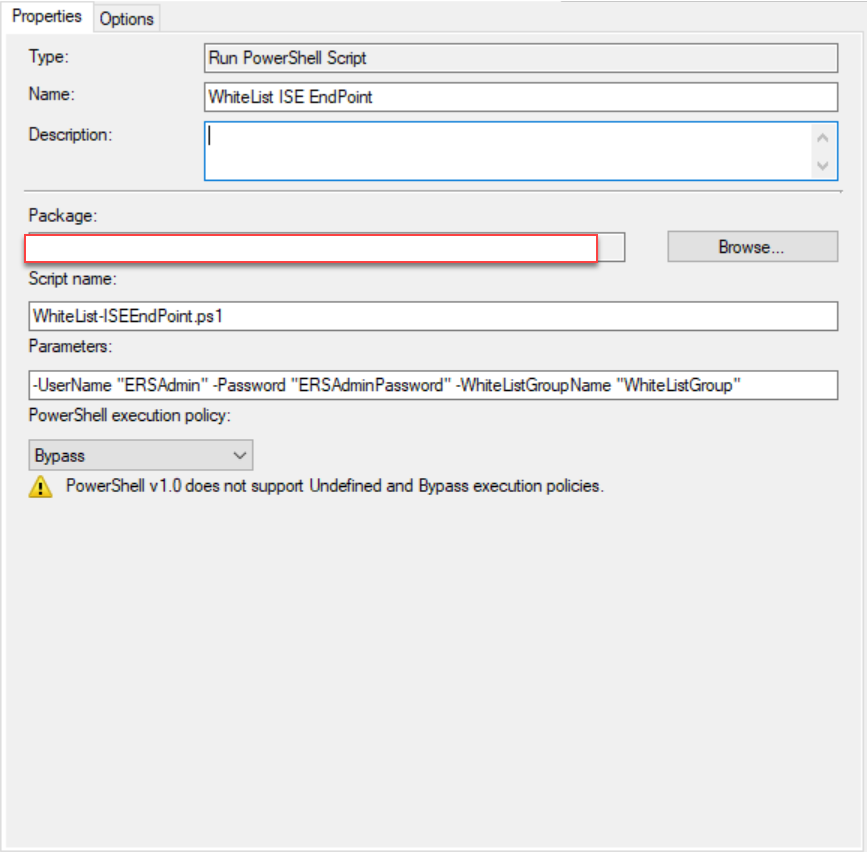
- Creates new EndPoint from MAC Address.
- Updates EndPoint’s Group to a special WhiteListing group that you specify.
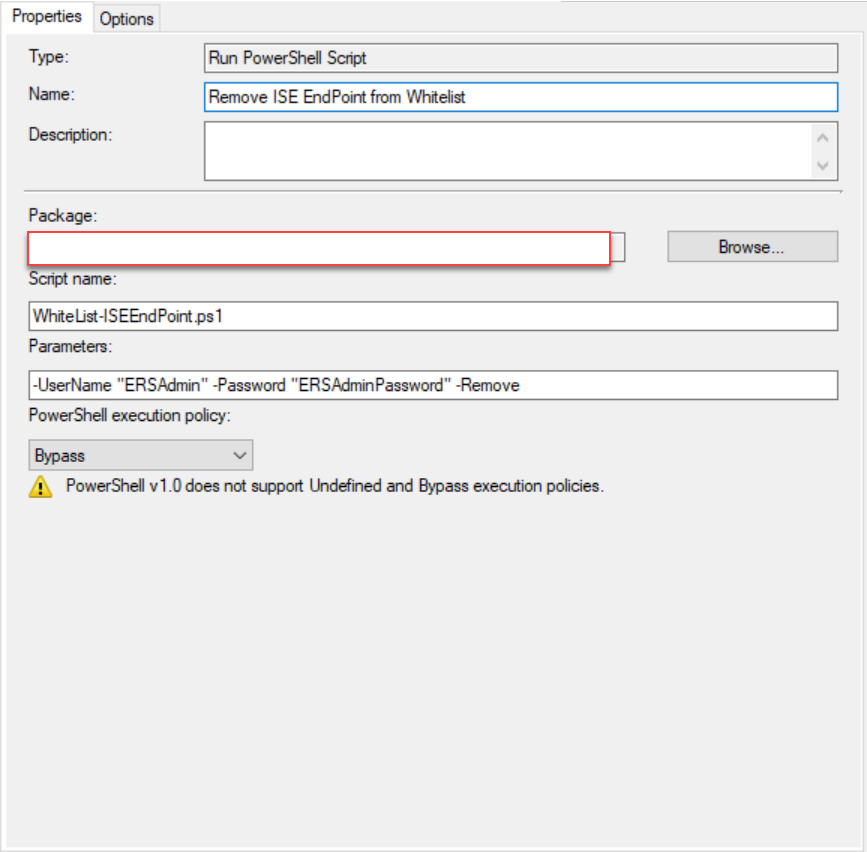
- Deletes the EndPoint’s MAC record from ISE.
You can download the whitelisting script and all related files from my GitHub repo. The length of the script made posting inline prohibitive.
Integrating the script into WinPE
If you followed the previous steps in this series, you should already have most if this in place. We are going to update the OSDInjection.XML file to include our new script and the ISEServers.txt file (optional). Before you do this, be sure that your script works and that you can add and remove a machine from your whitelisting group. I suggest booting into WinPE then running the script from a USB to test.
If you want details on how to edit your OSDInjection.XML and winpeshl.ini files, please refer to the previous posts in this series. Also, I’ve included sample files in the GitHub repo with the whitelisting script. Note: I tested adding the script to a new boot image and kept getting SSL errors from the script. I added my root cert to the media boot image (just like in the machine auth setup) and it resolved the issue. Plus it adds an extra level of security.
Updating your Upgrade Task Sequence
Simply add a Run PowerShell Script step to the beginning of your Task Sequence to launch the script.
Add a second Run PowerShell Script step to the end of your Task Sequence to remove the MAC endpoint from ISE.
You may also consider importing your 802.1x GPO settings at this point, but once you’ve joined your machine to the domain and the machine cert is created (assuming you use machine certs for auth), it should automatically get configured in ISE. You should be able to remove the custom Unattend.XML, SetupComplete and SetupRollback entries that you added in the previous steps in the series and just rely on the ERS whitelist to handle auth.
Summary
Sorry if this isn’t a full step-by-step of the complete process. I just needed to get this information and the script out for people to begin working with. If you have questions or concerns, please feel free to reach out to me here on on Twitter (@AdamGrossTX) and I’ll see what I can do to help.
In case you missed the link above you can download everything from my GitHub repo Here
Don’t forget to check out the Tips & Tricks page.